Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ariyoshi, Gen; Obayashi, Hironari; Saito, Shigeru; Sasa, Toshinobu
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
To clarify the flow characteristics of heavy liquid-metal (HLM) is important to achieve the construction of nuclear transmutation facility that utilizes HLM as a spallation target and coolant. At present, lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) spallation target plans to be installed in Japan proton accelerator research complex (J-PARC). LBE is also selected as one of the candidate media of a spallation target and a coolant for innovative nuclear systems such as accelerator-driven system (ADS) and LBE-cooled fast reactor, due to its adequate physical/chemical properties. The characteristics of LBE flowing inside the target are usually clarified with computational fluid dynamics analysis since the measurement techniques for the HLM flow are not well established, especially for high temperature region over 450 C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480
C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480 C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
Kume, Etsuo; Kitamura, Tatsuaki*; Takase, Kazuyuki; Ose, Yasuo*
Kashika Joho Gakkai-Shi, 25(Suppl.2), p.369 - 370, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
Ose, Yasuo*; Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kano, Takuma; Akimoto, Hajime
Dai-18-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Yoshishu (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*
Proceedings of 1st International Forum on Heat Transfer (IFHT 2004), p.207 - 208, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*
Dai-23-Kai Nihon Shimyureshon Gakkai Taikai Happyo Rombunshu, p.121 - 124, 2004/06
no abstracts in English
Ose, Yasuo*; Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kano, Takuma; Kureta, Masatoshi; Akimoto, Hajime
Dai-41-Kai Nihon Dennetsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, 2 Pages, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Nishimura, Kiyohiko*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*
Annual Report of National Institute for Fusion Science; April 2003 - March 2004, P. 12, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Higashijima, Satoru; Oyama, Naoyuki; Bruskin, L. G.; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Shirai, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hill, K. W.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1235 - 1245, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:88.59(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Takenaga, Hidenobu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(8), p.790 - 804, 2003/08
no abstracts in English
Kuroda, Hiroshi*; Isoda, Yutaka*; Onishi, Mitsuyo*; Iwahashi, Masayuki*; Sato, Chizuru*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Ito, Toshimichi; Iseda, Kenichi*; Nishizawa, Keisuke*; Shima, Shigeki*; et al.
Umi No Kenkyu, 12(2), p.195 - 214, 2003/03
Variabilities of the periodical current fluctuations on the shelf in Hidaka Bay were examined with use of ferry-mounted ADCP data obtained during 2000-2001. As the result of analysis, (1) three periodical variations around 10-, 25- and 60-day period are found, (2) the horizontal phase lag of these variations is little along the ship track, and the vertical phase lag is little at 10- and 25-day variations while several-day at 60-day variation, and (3) the 10-day variation shows coherent cross-correlation between current and wind.
Maki, Akira; ; Taguchi, Katsuya; ; Shimizu, Ryo; Shoji, Kenji;
JNC TN8410 2001-012, 185 Pages, 2001/04
"The third technological meeting of Tokai Reprocessing plant (TRP)" was held in JNFL Rokkasyo site on March 14 , 2001. The technical meetings have been held in the past two times. The first one was about the present status and future plan of the TRP and second one was about safety evaluation work on the TRP. At this time, the meeting focussed on the corrosion experrience, in-service inspection technology and future maintenance plan. The report contains the proceedings, transparancies and questionnaires of the meeting are contained.
, 2001. The technical meetings have been held in the past two times. The first one was about the present status and future plan of the TRP and second one was about safety evaluation work on the TRP. At this time, the meeting focussed on the corrosion experrience, in-service inspection technology and future maintenance plan. The report contains the proceedings, transparancies and questionnaires of the meeting are contained.
Nakayama, Oukatsu;
JNC TN9400 2000-087, 74 Pages, 2000/07
We have been developing an Ultrasound Doppler Velocimetry technique (UDV), in order to apply thermo-hydraulic measurement in sodium. A feasibility study had been conducted to identify development subjects of sensor and signal processing. Thus, high temperature ultrasonic transducers were manufactured to use in water and sodium tests, which will be scheduled to optimize an algorism of signal processing and to improve the characteristic of the transducer. ln this report, we described the results of an experiment on the acoustic characteristic of transducer in water. The results are as follows : (1)The ultrasound beam profile of the transducer relating to the characteristic of velocity profile measurement using scattering ultrasound wave was obtained. The estimation of ultrasound beam profile in liquid and an ultrasound near-field region were introduced from these experimental data, (2)lt was confirmed that the frequency's spectrum of transducers are adequate for the design requirement of flow velocity range. The specifications of a transmitter and receiver for a transducer were identified, such as the amplitude gain for scattered ultrasound signal and the frequency resolution for Doppler sift signal. (3)The spatial resolution of the ultrasound beam was estimated to evaluate the accuracy of now profile measurement on UDV system.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; ; ; ; Kamide, Hideki; Tokuhiro, Akira; Hishida, Koichi
JNC TN9400 2000-057, 60 Pages, 2000/05
ln experimental study for the thermohydraulics of fast reactor, a simple experiment with fine measurement has been desired for understanding of phenomena and for verification of computer code rather than mockup experiments of large scale. For such purposes quality of experimental data must be improved. ln the velocity measurement, instantaneous velocity profile will have great advances for the understanding of phenomena and for the verification of computer code. ln this report two methods of the velocity profile measurement are discussed; one is ultrasound Doppler velocimetry (UDV) and the other is particle image velocimetry (PIV). These methods were applied to water experiments. The UDV was applied to pipe flow, planer jet, and the inter-wrapper flow which is seen in the gap region between subassemblies of fast reactor core. Cross check with laser Doppler velocimetly showed proper measurement of the UDV. Problems including the application to sodium experiments are also discussed. The PIV was also applied to the inter-wrapper flow. For the application to complex flow geometry, noise reduction method was developed to improve the measurement accuracy.
Kimura, Nobuyuki; Tokuhiro, Akira; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2000-027, 181 Pages, 2000/02
A quantitative evaluation on thermal striping, in which temperature fluctuation due to convective mixing among jets causes thermal fatigue in structural components, is of importance for reactor safety. ln this study, a water experiment was performed using vertical and parallel triple jets, those are cold jet on center and hot jets on both side. The experimental parameter was discharged velocity of the triple-jet and local temperature and velocity were measured by ultrasound Doppler velocimetry and movable thermocouples. The objective is a quantification of the mixing process in the multiple-jet. Under isovelocity condition, the jets oscillated periodically and mixing among thejets was promoted by periodic oscillation. The periodic oscillation was dependent on the Strouhal number based on the discharged velocity. Under non-isovelocity condition, on the other hand, the jets did not oscillate periodically and mixing among the jets progressed more gentle compared with the case under isovelocity condition. The tempwrature fluctuation could be decomposed into coherent and random components using the phase averaging process. The rate of the coherent component in the temperature fluctuation increased and the rate of random component in temperature fluctuation decreased in proportion as the discharged velocity was increased.
Yang Zumao*;
JNC TN9400 2000-009, 81 Pages, 2000/02
It is important to study thermal stratification and striping phenomena for they can induce thermal fatigue failure of structures. This presentation uses the AQUA code, which has been developed in Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), to investigate the characteristics of these thermal phenomena in water, liquid sodium, liquid lead and carbon dioxide gas. There are altogether eight calculated cases with same Richardson number and initial inlet hot velocity in thermal stratification calculations, in which four cases have same velocity difference between inlet hot and cold fluid, the other four cases with same temperature difference. The calculated results show : (1) The fluid's properties and initial conditions have considerable effects on thermal stratification, which is decided by the combination of such as thermal conduction, viscous dissipation and buoyant force, etc., and (2) The gas has distinctive thermal stratification characteristics from those of liquid because for
JNC TN9400 2000-008, 323 Pages, 2000/02
This rport presents numerical results on theemal striping characteristics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm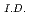 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe, and four parameters, j.e., (1)diameter ratio
elbow and a branch pipe, and four parameters, j.e., (1)diameter ratio  between both the pipes, (2)flow velocity ratio
between both the pipes, (2)flow velocity ratio  between both the pipes, (3)angle
between both the pipes, (3)angle  between both the pipes, and (4)Reynolds number Re. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)According to the decreasing of the diameter ratio, significant area of second-order moments was expanded in the fixed condition of
between both the pipes, and (4)Reynolds number Re. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)According to the decreasing of the diameter ratio, significant area of second-order moments was expanded in the fixed condition of  =1.0. (2)Significant second-order moments area was expanded for the increasing of the flow velocity ratio
=1.0. (2)Significant second-order moments area was expanded for the increasing of the flow velocity ratio  specified by varying of the main pipe velocity in the case of a
specified by varying of the main pipe velocity in the case of a  = 1.0 constant condition. 0n the other hand, the area was expanded for the decreasing of the velocity ratio
= 1.0 constant condition. 0n the other hand, the area was expanded for the decreasing of the velocity ratio  defined by varying of the branch pipe velocity in the case of a
defined by varying of the branch pipe velocity in the case of a  = 3.0 constant condition. (3)Maximum second-order moments values were generated in the case of
= 3.0 constant condition. (3)Maximum second-order moments values were generated in the case of  = 180
= 180 due to the influence of interactions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe. (4)According to the increase of Reynolds number, significant area of second-order moments was expanded due to the activation of turbulence mixing in the main pipe.
due to the influence of interactions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe. (4)According to the increase of Reynolds number, significant area of second-order moments was expanded due to the activation of turbulence mixing in the main pipe.
Ikeda, Takao*; Yoshida, Hideji*
JNC TJ7400 2000-006, 159 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
Miyake, Yasuhiro*; *; ; Kimura, Nobuyuki
JNC TN9400 2000-016, 40 Pages, 1999/12
ln the conventional visualization system for the computational results, only Japanese (Nihongo) Line Printer (NLP) was available to print two dimensional cross sectional plots of vector and scalar fields. To evaluate the phenomena, an analyst had to print many plots on the NLP. This task makes difficult to check the computational results immediately after the calculation. Recently, as the visualization tools, we introduced Micro AVS and Field View which are utilized widely in the scientific and the industrial fields. ln order to show the numerical results on the visualization software, we constructed a post processing system which convert the results of the numerical code to "lntermediate files" which can be read by the visualization tools. As using this system, the examination of the numerical results can be executed on the display of the personal computer. Furthermore, the persuasive report and paper with high quality can be produced due to the color printing. As for the transient calculation, the change of the phenomena can be visually evaluated by using the animation function.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagashima, Keisuke; Sakasai, Akira; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kubo, Hirotaka; Higashijima, Satoru; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 39(11Y), p.1917 - 1928, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.65(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Tokuhiro, Akira; Kimura, Nobuyuki;
JNC TN9400 2000-014, 86 Pages, 1999/06
Experiments were performed using the WAJECO facility to investigate the thermohydraulic mixing of multiple jets flowing out of a LMFBR core. Mixing is the root of the thermal striping problem. The multiple jets are typically at different velocities and temperatures and may induce thermal stresses upon components they impinge. In our study we modeled the mixing of three vertical jets, the central at a lower temperature than the two adjacent jets at equal temperatures. The jets are quasi-planar. The parameters were the average exit jet velocities (Uo,av) and the temperature difference between the "cold" and "hot" jets ( Thc=Thot-Tcold). Measurements of the liquid velocity, initially using laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) and later ultrasound Doppler velocimetry (UDV), for both our reference single-jet and the triple-jet configuration, comprised Phase I of the experiments (up to 1994). Two reports (TN9410 96-181 and TN9410 96-296; in Japanese) reported on the hydraulic and heat tra
Thc=Thot-Tcold). Measurements of the liquid velocity, initially using laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) and later ultrasound Doppler velocimetry (UDV), for both our reference single-jet and the triple-jet configuration, comprised Phase I of the experiments (up to 1994). Two reports (TN9410 96-181 and TN9410 96-296; in Japanese) reported on the hydraulic and heat tra